 Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Preliminary study on alternative magnetic layout (AML) for tokamaks…
A new approach to tokamaks: the study on the Alternative Magnetic Layout (AML) and the TRUST project
Research on nuclear fusion aims to make reactors more compact, efficient, and easier to build. In this context, a group of researchers from the University of Tuscia has published a preliminary study in [1] introducing a new magnetic confinement scheme, called Alternative Magnetic Layout (AML).
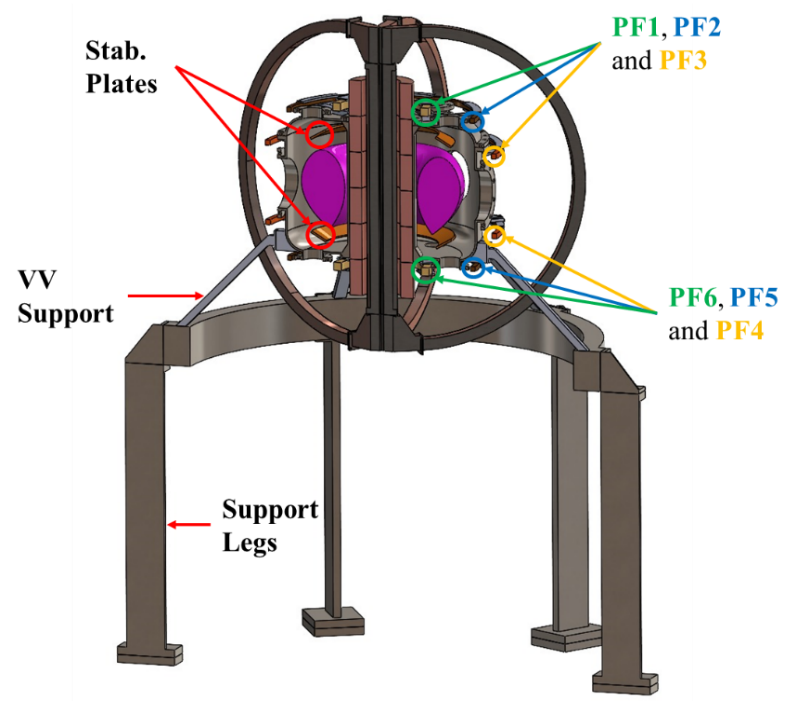
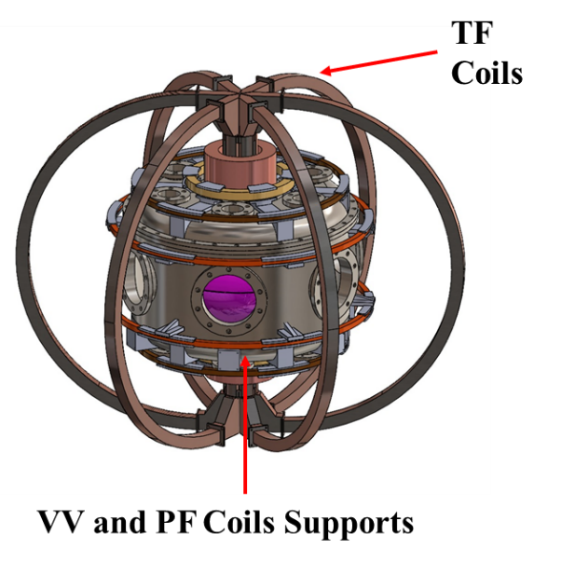
The idea is innovative: moving the central solenoid (CS) around the central column of the toroidal field coils (TF). This configuration reduces the reactor’s radial size, making it more compact. To compensate for the increased magnetic field required, high-temperature superconductors (HTS) are envisioned for the coils, capable of carrying higher currents and sustaining stronger fields compared to traditional superconductors.
The study shows that this solution is technically feasible, although engineering challenges remain in terms of assembly, electromagnetic force management, and integration of components. Some of the advantages include:
- better efficiency in the use of internal space;
- the possibility of placing poloidal field coils closer to the plasma, improving control and stability;
- potential cost reduction and easier maintenance.
This concept will be tested in the Tuscia Research University Small Tokamak (TRUST), a new university tokamak under construction in Viterbo. TRUST will be a flexible, low-cost experimental platform designed to train future fusion engineers and test innovative technologies and materials.
In conclusion, AML represents a promising proposal for the future of fusion reactors: a more compact design, aimed at both academic research and technology transfer to industry.
References: